eCommerce fulfillment encompasses a range of models that can vary widely based on factors like order volume, inventory levels, and processing needs. Depending on these parameters, businesses have access to diverse fulfillment methods, each with its own pros and cons. Ultimately, the optimal fulfillment approach is highly customized to the specific requirements of the business.

1) Storage Services – Warehousing
eCommerce fulfillmentEfficient storage solutions offering secure, organized, and accessible warehousing services.
- Secure Facilities: Ensuring protection against theft, damage, and environmental factors.
- Inventory Management: Systematic tracking and organization of stored goods.
- Flexible Space: Varied storage options to accommodate different types of products.
- Accessibility: Easy access to stored items for timely retrieval and distribution.
- Climate Control: Temperature and humidity regulation for sensitive products.
- Cost Efficiency: Scalable solutions to match storage needs and budgets.
- 24/7 Monitoring: Continuous surveillance and security measures.
- Logistics Support: Integration with transportation and distribution networks.
- Custom Solutions: Tailored services to meet specific business requirements.
- Professional Staff: Experienced personnel managing warehousing operations and customer service.
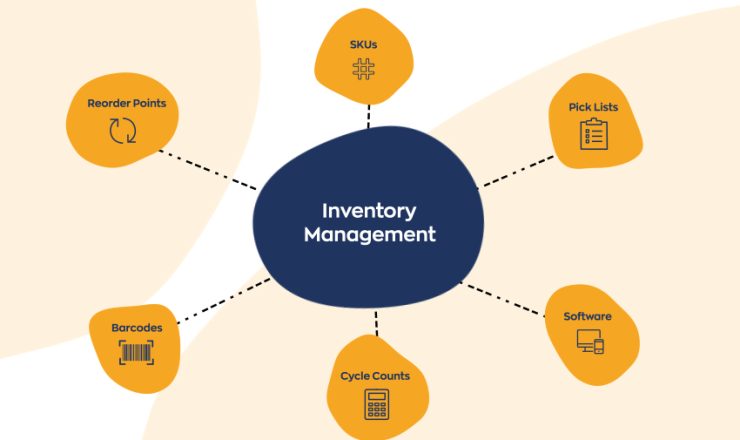
2) Inventory Management
Out Of StockTracking, organizing, and controlling stock levels for optimal efficiency.
- Stock Tracking: Monitoring quantities of products in real-time.
- Order Management: Handling and processing purchase orders and sales orders.
- Demand Forecasting: Predicting future inventory needs based on trends and data.
- Reorder Levels: Setting minimum stock levels to trigger new orders.
- Warehouse Organization: Structuring storage to optimize space and accessibility.
- Inventory Valuation: Calculating the value of inventory for financial reporting.
- Stock Audits: Regular checks to ensure accuracy of inventory records.
- Supplier Management: Coordinating with suppliers for timely restocking.
- Data Analysis: Using analytics to improve inventory control and decision-making.
- Technology Integration: Utilizing software systems for automation and efficiency.
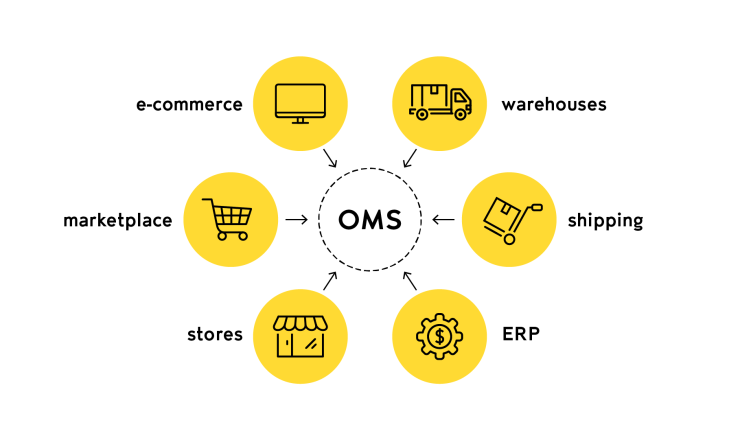
3) Order Management
eCommerce websiteProcessing, tracking, and fulfilling customer orders efficiently and accurately.

4) Order Picking & Packaging
PackagingSelecting items and preparing them for shipment with accuracy.
- Order Selection: Identifying and retrieving items from inventory based on orders.
- Picking Accuracy: Ensuring correct items and quantities are selected for each order.
- Efficient Layout: Organizing storage areas to streamline picking processes.
- Barcode Scanning: Using technology to verify items and reduce errors.
- Packing Materials: Using appropriate materials to protect items during shipping.
- Order Assembly: Combining items into packages according to order specifications.
- Labeling: Generating and affixing shipping labels and documentation for each package.
- Quality Checks: Inspecting items and packaging to ensure they meet standards.
- Shipping Preparation: Sorting packages based on delivery methods and destinations.
- Tracking Integration: Updating order status and tracking information for customer visibility.

5) Shipping & Logistics
Best courier partnerCoordinating transportation, delivery, and management of goods efficiently.
- Transportation Management: Coordinating the movement of goods from origin to destination.
- Route Optimization: Planning the most efficient routes to minimize transit time and costs.
- Carrier Selection: Choosing appropriate carriers based on cost, speed, and reliability.
- Freight Management: Handling various types of cargo, including bulk, special, and hazardous materials.
- Warehouse Coordination: Integrating shipping processes with warehousing operations for smooth transitions.
- Inventory Management: Monitoring stock levels to ensure timely fulfillment of orders.
- Customs and Compliance: Managing regulations and documentation for international shipping.
- Tracking and Visibility: Providing real-time updates on shipment status and location.
- Packaging Solutions: Ensuring goods are packaged securely and appropriately for transportation.
- Returns Handling: Managing reverse logistics for returns, exchanges, and product recalls.

6) Returns Management
Return ordersHandling product returns, exchanges, and refunds efficiently and accurately.

